Just think about what happens when your Mom or Dad calls you for dinner?
At that time, you can hear them asking you to wash your hands before coming to eat, you feel the water and soap against your skin, you can smell what’s cooking, and finally taste the food on your plate.
You can purchase the latest hearing aids at a fair price through HearingSol, If you need any assistance or you have a query regarding The Five Senses of The Human Body or Hearing Loss, feel free to call us at +91-9327901950. We are always here to help you.
This is all because of your working five senses.
Living creatures are an amazing miracle of God’s creation. From the very beginning, God created the earth. Subsequently, God created the “LIFE” and “HUMAN“ which became the most powerful creatures on the earth due to his wondrous power of SENSATION.
Normally, a sense is a physiological capacity or conscious awareness of organisms that supply information for perception. Apparently, the senses allow us to experience the world around us. It might be unimaginable to live our lives without our five sense organs.
What do you understand by the sense?
The most appropriate definition of the sense is the system having a group of sensory neural cell types that respond when a physical phenomenon occurs, and that corresponds to a particular group of regions inside the brain where these signals are transmitted, received, and interpreted.
The main tool for the human body is the five senses which they use to perceive the world. Our brain receives signals from each of these organs and interprets them to give us a sense of what’s happening around us. There are more senses in the body like the perception of pain, heat, balance, and pressure. But the basics are five.
What is the importance of sense organs?
All of the senses in the human body is very important but the most important five sense organs that are the ear, eye, nose, skin, and tongue play a crucial role in a human’s life. If any of the senses among the five is damaged then a person will have to face a lot of difficulties in life.
In our daily life senses plays a very important role. At every moment in our life, we use at least use one of our senses. A human touch, feel, taste, see, and smell at every point of life to function properly or adapt to a new environment. All the sense organs are coordinated with each other to function properly.
These sense organs connected to the CPU of the human body known as the brain. The sense organs carry all the information from the environment and send it to the brain and the brain processes this information and let you know what you are smelling, hearing, tasting, seeing and, feeling.
What are the five senses organs of a human body?
The nervous system of our body receives and processes the information and later, relays the signals to the brain in order to react with the world. Much of this information reaches us through the 5 senses organs. Those are the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin. However, Sight (vision) must be the most delightful of all the senses. But touch (skin) comes before sight, or even before speech. It is the first expression and the last, and it always mentions the truth.
There are different receptors in each sense organs. One is general receptors and the other is special receptors.
- The skin contains general receptors
- Mouth and nose contain a special receptor that is called chemo-receptors (chemical receptors)
- Eyes also contain a special receptor known as photo-receptors (light receptors)
- Ears contain mechanoreceptors which are also a special receptor.
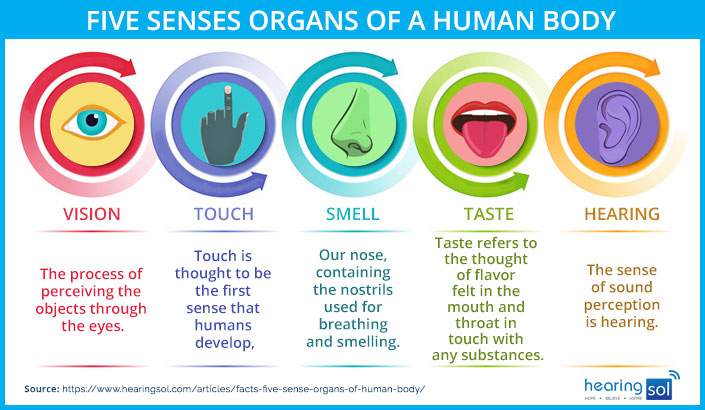
All human senses organs consist of – eye, ears, nose, tongue, and skin. And they provide the sense of sight, hearing, smell, taste, and touch respectively. Let’s discuss these five senses in detail.
1 The sense of SIGHT (Ophthalmoception)
The process of perceiving the objects through the eyes is called as sight. Let’s discuss the mechanism of sight.
An eye is an organ responsible for the vision to detects visible images and most use more than any other sense. The light reflects off an object to the eye. The transparent outer layer of the eye called the cornea bends the light that passes through the hole of the pupil. The iris (which is the colored part of the eye) works like the shutter of a camera, retracting to shut out light or opening wider to let in more light. An eye translates light into image signals for the brain through the various parts like sclera, the cornea, anterior & posterior chambers, iris, pupil, lens, vitreous humor, retina, fovea, macula, and the ophthalmoscope.
The iris is the colored part of the eye which actually is a pigmented muscle that controls the size of the pupil. The pupil dilates to allow more light into the eye or contracts to allow less light into the eye. Cornea covered both iris and pupil. The cones and the rods are the two types of light-sensitive cells in the retina. When the cones distinguish colors, the rods allow us to see better in dim light. And, by the optic nerve, all of this information is sent to the brain.
The images actually sent are upside down but our brain helps to understand what it is by turning the image on the right side up.
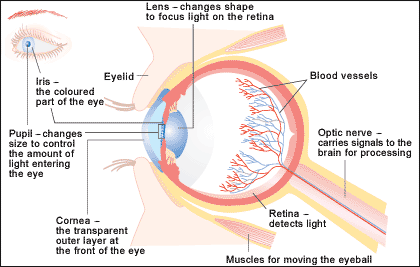
The different parts of sense organ: Eye
- The sclera: The part of the eye that is white is the sclera. It is the outermost part of the eye which is quite hard and helps to maintain the shape of the eye. The transparent cornea at the front of the eye is formed by the sclera.
- The cornea: The transparent covering at the front of the eye is known as the cornea. The light rays entering the get bent with the help of the cornea.
- The Iris: The colored part of the eye is known as the iris. The iris helps in controlling the size of the pupil so that the more light enters the eye and it also helps in bending the light rays.
- The Pupil: The pupil is the dark opening in the center of the eye through which the light enters the eye. The pupil can increase or decrease its size according to its needs. In the dim light, it increases its size so that more light enters the eye and in bright light, it decreases its size so that less light enters the eye.
- The Lens: The lens is the biconvex lens that bends the light entering into the eye. Its function is to focus the images on the backside of the retina. It can also change its shape according to the distance of the object.
- The Retina: The inner layer of the eye is called the retina. It contains the cells that are sensitive to the light.
- The Optic nerve: The optic nerve carries the messages from the retina to the brain.
- The Choroid: The choroid is the middle layer of the eye. The nutrients to the eye are transferred through the blood vessels that are contained inside the choroid.
Problem with ophthalmoception
The inability to see is blindness, results from any damage to any part of the eyes. It may be partial or whole. Cleaning of the eyes, eye drops, surgery, and laser treatments available to cure severe vision impairment.
Caring for the sense organ: EYE
- Do not rub the eye with dirty hands.
- Rest the eyes when reading, watching television, sewing, or using the computer.
- Do not wear prescription glasses that do not belong to you.
- If harmful chemicals get into the eye, remove it by washing with a lot of water Use a clean cloth to remove solid objects from the surface of the eye.
- Use proper lighting when reading or doing close-up work.
- Visit the optician or eye specialist at least once every two years.
2 The sense of HEARING (Audioception)
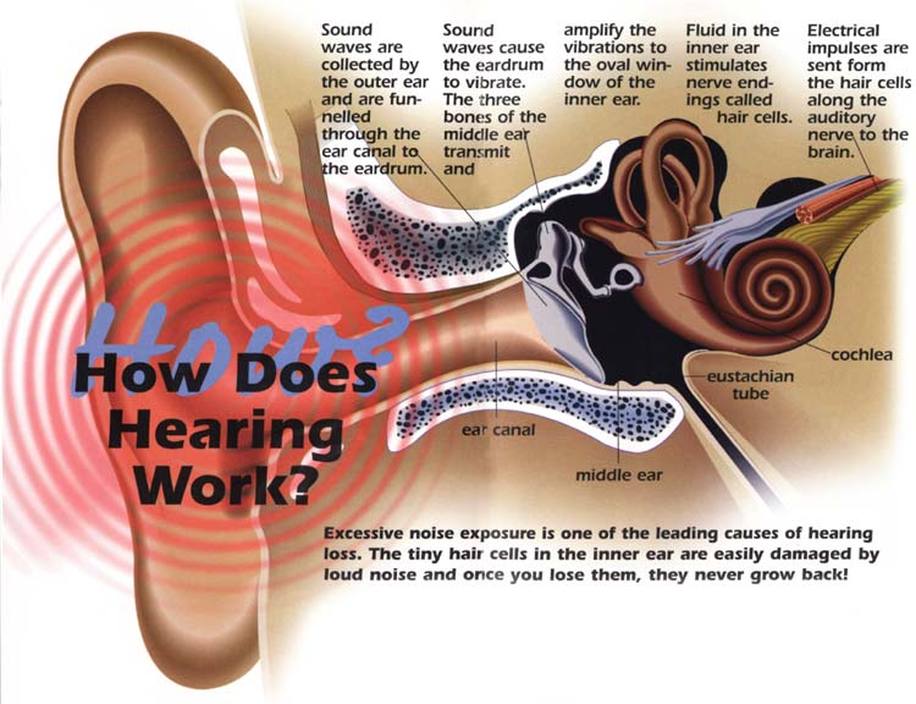
The sense of sound perception is hearing. Our ears help us to hear. It is divided into 3 parts i.e. the outer ear, middle ear, and the inner ear. The ear uses bones, hairs, and fluid to convert sound waves into sound signals. The hearing is the mechanical motion of the vibrations detected in the inner ear through a series of tiny bones to tiny hairs.
The different parts of sense organ: EAR
- Outer ear: The 5 sense organs include outer ear consists of the parts pinna and ear canal. The main function of the outer ear is to collect the sound from the surrounding and direct them to the middle canal. The pinna is the soft tissue that makes the visible part of the ear and the ear canal is the passage through which the sound is directed to the middle ear.
- Middle Ear: This is the middle part of the ear that starts with the tympanic membrane which is also known as the eardrum whose function is to vibrate when there is a difference in pressure caused due to soundwaves.
- Inner Ear: The inner ear is the deepest part of the ear that consists of the cochlea. The cochlea is the organ that converts the mechanical sound vibrations to the nerve signals and then transmits it to the auditory nerve.
- The Vestibule: The vestibule consists of the semicircular canals is an organ that helps in providing us a sense of balance, direction, and, spatial orientation.
Lets have a look on the mechanism of hearing
At first sound wave hits the eardrum, then the eardrum makes the tiny bones like the malleus, incus, and the stapes moves. Mechanoreceptors picked this movement in the inner ear. These receptors exist on hair cells and it contains cilia between the vestibule and the end of the semicircular canals. As cilia move, an impulse is created by the cells that are sent to the eight cranial nerve through the cochlea. The cranial nerve carries the impulse to the nerve and then the brain interprets the information as a valid sound.
Problem with Audioception
Hearing impairment or deafness is the inability of hearing. Few medications, therapies, and surgeries are recommended to cure hearing. While, in some cases, hearing aid also helpful for severe deafness to some extent.
Some impaired people are able to determine the direction and location of vibrations picked up through the feet.
Caring of the ear
- Stay away from the large volumes.
- Do not put the stick into your ears.
- Do not let water enter your ears.
- Your diet should contain magnesium and vitamin B rich foods.
- Take caffeine in a limited amount.
- Give a regular visit to the audiologist.
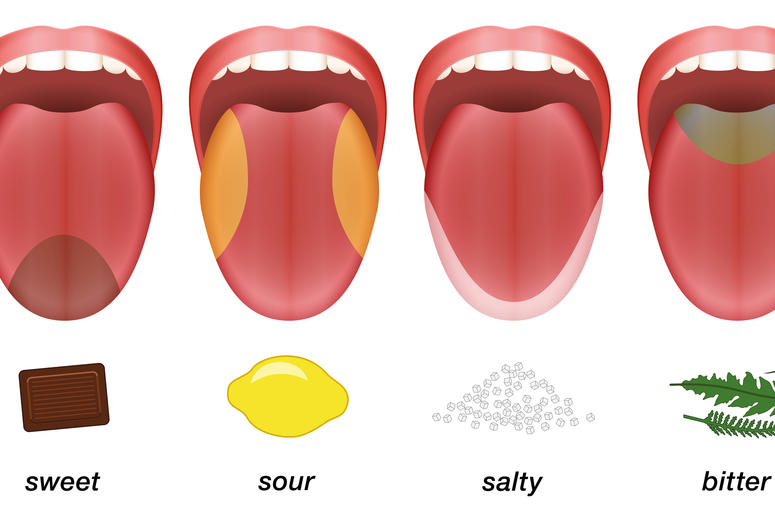
3 The sense of TASTE (Gustation)
Taste is sensed in the taste buds. Adults have 2,000 to 4,000 taste buds.
Taste refers to the thought of flavor felt in the mouth and throat in touch with any substances such as food, certain minerals, chemicals, and toxin, etc. Remember it is fully different from the sense of smell. Taste buds, sensory organs on the top of the tongue, or mouth connected to nerves in the brain. Taste buds contain chemo-receptors. The taste buds actually lie down in the grooves between each papilla. The papilla is the little bumps on the tongues.
When food touches the taste buds, it activates nerve receptors which later send signals to facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves. Those nerves carry the signals to the medulla oblongata, which deliver them to the cerebral cortex of the brain. There are five basic tastes: saltiness, sourness, sweetness, bitterness, and umami. In addition, a taste sense depends on other senses and factors, including smell, texture, and temperature.
There is also a fifth taste, defined as umami or savory. There may be many other flavors that have not yet been discovered. Also, spicy is not a taste. It is actually a pain signal, according to the National Library of Medicine (NLM).
Problem with Gustation
The incapability to taste is called ageusia. Certain medications may help to treat ageusia e.g. Topical anti-fungal or antibiotics: candidiasis/oral infections.
4 The sense of SMELL (Olfaction)
Humans may be able to smell over 1 trillion scents, according to researchers. Research published in the May 11, 2017, issue of the journal Science suggests that humans can discriminate among 1 trillion different odors; it was once believed that humans could take in only 10,000 different smells.
Our nose, containing the nostrils used for breathing and smelling. Without it, we couldn’t able to enjoy our favorite smells like a fragrance of cooking, a bouquet of flowers, and perfumes, etc. Olfaction, a sense of smell, has a minimum of 390 olfactory receptors at the top of the nasal cavity. The olfactory cells are chemo-receptors, these protein receptors can detect subtle differences in chemicals. You can smell with the olfactory cleft, which is found on the roof of the nasal cavity, next to the “smelling” part of the brain, the olfactory bulb, and fossa.
When inhaled, those triggers a signal that travels to the olfactory bulbs through the epithelium. The olfactory bulbs contain neuron cell bodies, they send the signal along the cranial nerves towards the cerebral cortex in the brain. Our sense of smell is able to determine seven types of sensations. Those are camphor, ether, musk, flower, mint, acrid, or putrid.
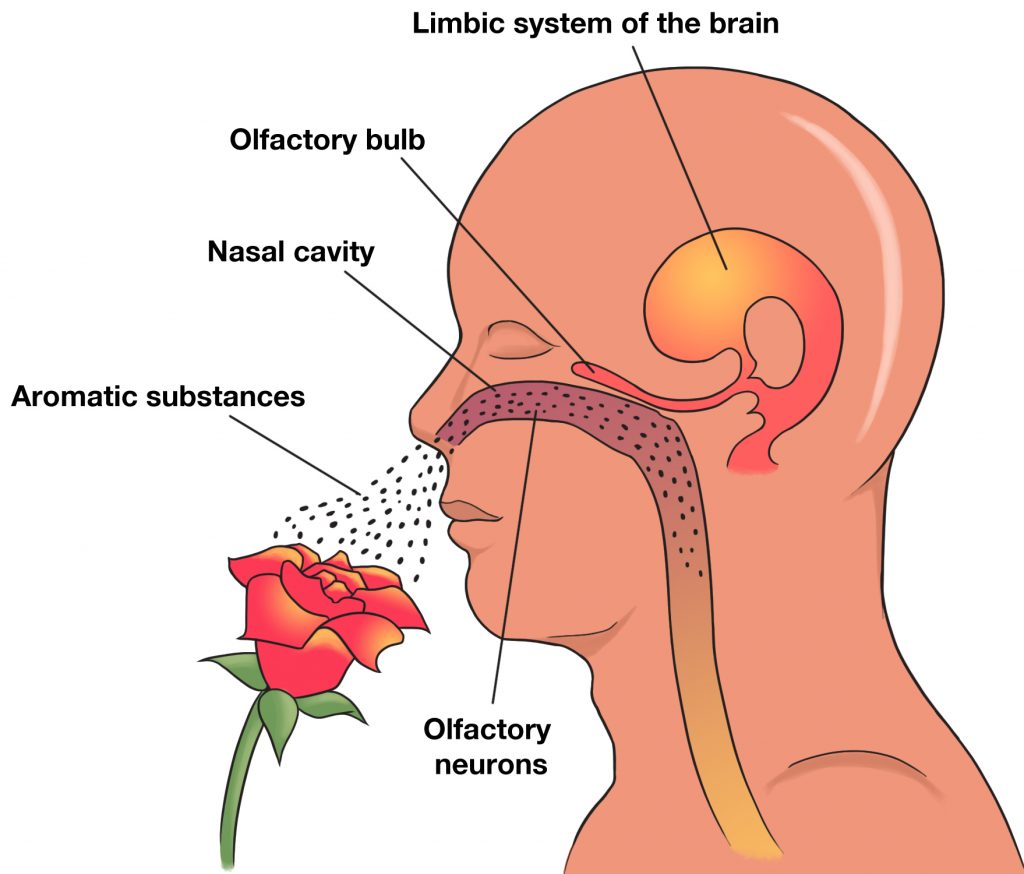
Different parts of the Nose:
- External nostrils: This part of the nose is the respiratory passage. The two holes of our nose through which the air passes to the nasal chambers.
- Nasal Chambers: The nasal chamber is the large cavity that is located above the buccal cavity and gets separated from the buccal cavity by the palate. It is separated into two parts right part and the left part by a nasal septum. It is divided into three regions- nasal vestibule, conditioner, and olfactory region.
- Olfactory Region: It is the upper part of the nasal chamber. The surface is yellow-brown. It helps in perceiving the sensation of smell.
Problem with Olfaction
Anosmia is the loss of the sense of smell. Intracranial theosophy spray and smell therapies help in improving the sense of smell. Poor smelling ability may be a symptom of schizophrenia and depression. It can be due to a medical condition or aging.
5 The sense of TOUCH (Somatosensation)
Touch is thought to be the first sense that humans develop, according to the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
Although the skin is the largest organ in our body, touch is perhaps the most unnoticed sense of the body. Nerve endings and specialized neural receptors in the skin (including hair follicles, tongue, throat, and mucous) send touch signals to the brain. Blind people can use their sense of touch to read Braille which is a type of reading or writing. Generally, touch sensation first develops in the 8 weeks of the gestation period.
The skin consists of three major tissue layers: the outer epidermis, middle dermis, and inner hypodermis. Specialized receptor cells within these layers detect tactile sensations and send those signals through peripheral nerves towards the brain. Receptors, for example, Merkel cells, are forms in the lower epidermis of lips, hands, and external genitalia. Similarly, Meissner corpuscles are found in the upper dermis of hairless skin such as fingertips, nipples, the soles of the feet. All of these receptors detect touch, pressure, and vibration.
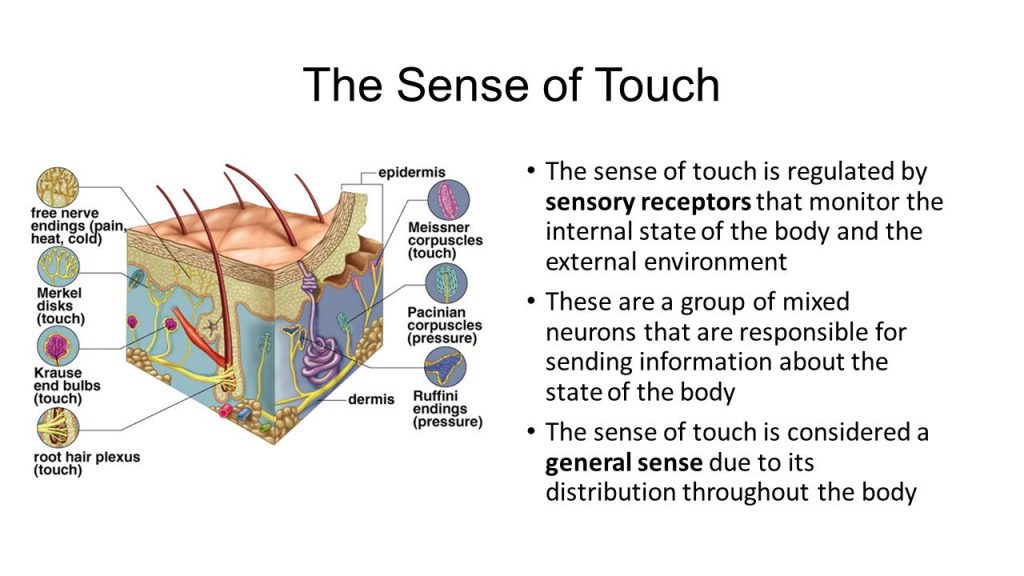
The different layers of skin
- The epidermis: The outer layer of the skin is called the epidermis. This outermost layer is waterproof the sense of the touch is at this layer.
- The dermis: This is a layer beneath the epidermis and contains tough connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands.
- The hypodermis: The deeper subcutaneous tissue is made of fat and connective tissue.
Problem with Somatosensation
Tactile anesthesia is the loss of the ability to feel anything touched. Paresthesia is a sensation of tingling, pricking, or numbness of the skin that occurs due to nerve damage.
Sensory System
It is a part of the nervous system. This is responsible for processing sensory information. It consists of sensory neurons and parts of the brain involved in sensory perception. The sensory system is recognized for vision, hearing, touch, taste, smell, and balance.
Other senses of the body
Apart from these, other senses like balance and acceleration, thermoception, proprioception, pain, sexual stimulation, and other internal senses are normally stimulated within the body that leads to enhancing the human’s life.
5 Senses Activities for Preschoolers
Children learning about the five senses is a great thematic unit for preschoolers. Young children are curious about the world around them and often use their senses to explore and learn. especially at the beginning of the year. There are many centers of teaching 5 senses. They deliver the opportunity to the children to play learn and discover in a way that is exciting.
They teach about one of the five senses each day during circle time. These are a few of their very favorite ideas for each station:
- Hearing – Water Xylophone | Learn Play Imagine
- Smell – Painting with Seasoning and Spices | Learn with Play at Home
- Touch – Stretchy Oobleck | Play to Learn Preschool
- Sight – Rainbow Discovery Bottles | Play to Learn Preschool
- Taste – Fun with Tasting Bottles | Gift of Curiosity
The 6th Sense of body – Sense of space
Proprioception can be termed as the sixth sense of the human body. It deals with how your brain understands where your body is in space. It includes the sense of movement and position of our limbs and muscles. For Example, a person can climb steps without looking at each one.
Balance and acceleration
It is the sense that allows an organism to sense body movement, direction, and acceleration, and to attain and maintain postural equilibrium and balance.
Thermoception
It is the sense of heat and the absence of heat (cold) by the skin and internal skin passages. It provides the parietal cortex of the brain with information on the movement and relative positions of the parts of the body. Neurologists test this sense by telling patients to close their eyes and touch their own nose with the tip of a finger.
Pain or Nociception
Physiological pain indicates nerve damage or damage to tissue. The three types of pain receptors are cutaneous (skin), somatic (joints and bones), and visceral (body organs). The main function of pain is to attract our attention to dangers and motivate us to avoid them. For example, humans avoid touching a sharp needle, or hot object, or extending an arm beyond a safe limit because it is dangerous, and thus hurts. Without pain, people could do many dangerous things without being aware of the dangers.
Sexual Stimulation
It is the stimulation that leads to, enhances and maintains sexual arousal, and may lead to orgasm. Distinct from the general sense of touch, sexual stimulation is strongly tied to hormonal activity and chemical triggers in the body. Although sexual arousal may arise without physical stimulation, achieving orgasm usually requires physical sexual stimulation.
All of the nerves in our body connect to the spinal cord (over our backbone), which attach to the brain. Hence, this very complex system is what allows us to sense things and thus makes our life wonderful.
We have 5 senses in our bodies. The 5 Senses interpret the world around us as we can find out and grasp whatever is happening around us. Watch this video to know more:
Some Amazing Facts of Sense Organs
Eyes
- Eyes can analyze approximately 36,000 pieces of information in an hour.
- During your whole lifetime, your eyes will process 24 million images approximately.
- Your one eyes consist of more than 2 million working parts.
- Eyes can detect light of a candle from miles away.
- The males are likely to affect color blind as compared to females.
- An average person blinks around 10 times in a minute when fully awake.
Nose
- 10,000 of different types of odors can be detected by your nose.
- Females have a tendency to smell well as compared to males.
- While pregnancy women`s sense of smell increases.
- 80% of taste is actually smelled.
- There are 10 million smell receptors present in the cavity behind the nose.
- An average person can differentiate between 4,000 to 10,000 smells.
Ears
- The earwax is pushed out by the cilia naturally which is present in the ear.
- The smallest bones are present in the ear.
- The earlobes of a person keep growing constantly.
- The eardrum of a person vibrates less than a billionth of an inch with respect to the sound.
Skin
- Skin is the largest sensory organ present in the human body.
- There are certain touch sensors present in the human body that do not send signals to the brain. These are called reflexes. Reflexes send the signal to muscles that respond quickly.
- Every 28 days of a cycle, your skin renews itself.
- In a minute skin around 30,000 dead cells sheds.
- During summer your skin excretes sweat around 3 gallons.
- The thinnest skin is of the eyelids which are about 0.02 mm thin.
- The thickest skin is of the feet which are about 1.44mm thick.
Taste
- An average person has 8000 taste buds.
- To differentiate between taste, the brain uses approx 20% taste buds and 80% smell receptors.
- The length of the tongue is about 3 inches.
- The tongue print is unique for every person.
- If you are suffering from cold then you could not get a good taste.
Outlook
A human body is so amazing that uses different sense organs to gather surrounding information. Our 5 Senses help us to observe and understand the world better. Not everyone is able to use all five of their senses. If someone cannot use any of these senses, they may be blind, deaf, or have any other disability.
You know what you can use all five of your senses simultaneously without even realizing it!
If you suspect any type of hearing loss, the very first step is to consult hearing care professional right away. So Book your schedule with us. Give us a call on our toll-free +91-9327901950.

 Reviewed by Mr. Ranjeet Kumar
Sr. Audiologist, Speech Therapist & Cochlear Implant Specialist, BASLP on
Reviewed by Mr. Ranjeet Kumar
Sr. Audiologist, Speech Therapist & Cochlear Implant Specialist, BASLP on