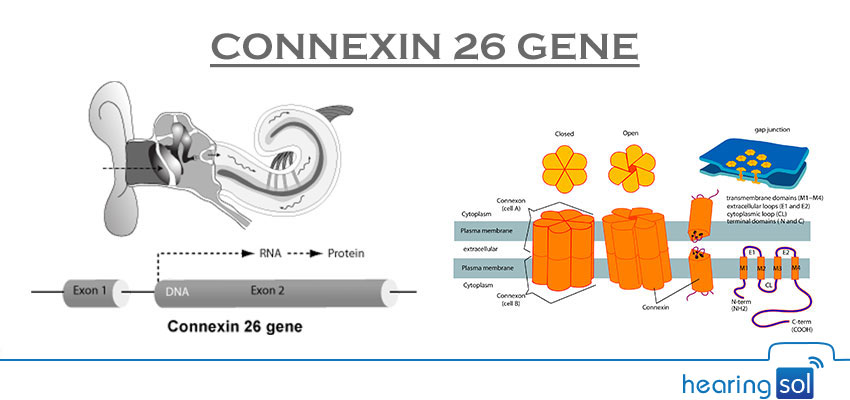
Connexin 26 is a protein that is commonly found in the GJB2 gene (gap junction protein beta 2) and is the most common cause of sensorineural hearing loss (damage to the neural pathways of hearing). If the CX26 protein is not enough then the inner ear potassium level will be too high and cause hearing damage.
You can purchase the latest hearing aids at a fair price through HearingSol, If you need any assistance or you have a query regarding Nonsyndromic Sensorineural Hearing Loss, feel free to call us at +91-9327901950. We are always here to help you.
What Is Connexin 26 (GJB2)
Connexin 26 alterations are responsible for at least 20 % of all genetic hearing loss and 10% of all the childhood hearing loss. Mutations in the gene (GJB2) encoding connexin 26 (cx26) is linked to sensorineural hearing loss either alone or as part of a syndrome. It affects the person’s high frequency, slowly progressive, bilateral, sensorineural hearing loss.
Connexin 26 mutations are non-syndromic, meaning that the mutation produces an only isolated hearing loss. It affects the child as they need specialized childcare before they are old enough to develop speech. Gap junctions made with connexin 26 transport potassium ions and certain small molecules, that permit the transport of nutrients, charged atoms (ions), and signaling molecules between adjoining cells.
Since cx26 and cx30 are co-localized within the inner ear, the effect of the dominant cx26 mutations on both of these wild-type proteins was determined. Connexin 26 mutations occur most often in Caucasian and Ashkenazi Jewish populations.
Other Name for Connexin 26 gene
- CX26
- CXB2_HUMAN
- DFNA3
- DFNB1
- gap junction protein, beta 2, 26kDa
- NSRD1
Gap Junctions – Definition & Function
Gap junctions are a type of cell junction in which adjacent cells are connected through protein channels. These are detected in connexin 32 in Charcot Marie Tooth-X linked to disease, in connexins 26 and 30 in deafness and skin diseases, and in connexins 46 and 50 in hereditary cataracts. When a cell starts to die from disease or injury, it sends signals through its gap junctions.
Gap junctions do an exchange of ions and small metabolites between adjacent cells and protein families (pannexins and connexins). Mutations in connexin genes cause a variety of genetic disorders, implicating a critical role in tissue homeostasis.
Related Biology Terms
Anchoring junction – A type of cell junction that is attached to components of the extracellular matrix and anchored to one another. In this junction, cells are connected by a mass of proteins.
Tight junction – A type of cell junction where two adjacent cells are tightly bonded to form a barrier. We can only find them inside vertebrates, animals with a backbone, and skeleton.
Plasmodesmata – Channels that connect the cytoplasm of adjacent plant cells.
Connexin – A family of proteins that makes up gap junctions.
Connexin 26 Treatment
Hearing loss due to mutations in GJB2 is present by birth but can vary in severity, from moderate to profound. The cochlea’s hybrid junction gaps, which facilitate intercellular communication, when one of the proteins is missing, the hybrid junction gaps fail to work, and the cochlea’s hair cells die off, leaving the body incapable of translating sounds into nerve impulses. Deafness at the time of birth may be caused by mutations in a specific gene known as Gap Junction Beta 2 (GJB2), which codes for the protein connexin 26.
Hearing loss related to Connexin 26 mutations is usually in the moderate to profound range. Research is currently finding the possibility of gene therapy to decrease the amount of hearing loss caused by Connexin 26 mutations or to eliminate it. This testing has mainly been conducted in mice and is many years away from practical human trials.
Need a specialized team to treat all of the issues associated with a Connexin 26 mutation. This group of individuals should include an Otologist or Otolaryngologists, audiologists, speech-language pathologists, a clinical geneticist, and a genetic counselor. HearingSol has a board-certified neurotologist, has performed thousands of successful hearing-related surgeries on children and adults, including many whose hearing impairment is due to a Connexin mutation.
You can purchase the latest hearing aids at a fair price through HearingSol, If you need any assistance or you have a query regarding Nonsyndromic Sensorineural Hearing Loss, feel free to call us at +91-9327901950. We are always here to help you.
Additional Information

 Reviewed by Mr. Ranjeet Kumar
Sr. Audiologist, Speech Therapist & Cochlear Implant Specialist, BASLP on
Reviewed by Mr. Ranjeet Kumar
Sr. Audiologist, Speech Therapist & Cochlear Implant Specialist, BASLP on