
You usually hear lots of suggestions on how to get away hiccups. Like “holding your breath for 10 seconds”, “putting sugar below your tongue” and the famous one is “Having a person jump out and scare you suddenly when you are not expecting it”.
If you need any assistance or have a question about Hiccups, you can consult our HearingSol experts with your problem, feel free to call us on +91-9327901950. We are always here to help you.
If you are hoping that these above factors can help to stop your hiccups than it’s our responsibility to inform you that there is no scientific proof that these remedies can actually work.
And if anyhow, these remedies found useful to you than maybe you can get rid of short time hiccups but if hiccups are not going away for a long time then you may be in an underlying medical condition.
In this article, we are going to find out what is the actual reason for hiccups, its risk/complication, and how to treat it with medicine as well as at home.
Wondering About Hiccups? Here Is The Explanation
What Is Hiccup?
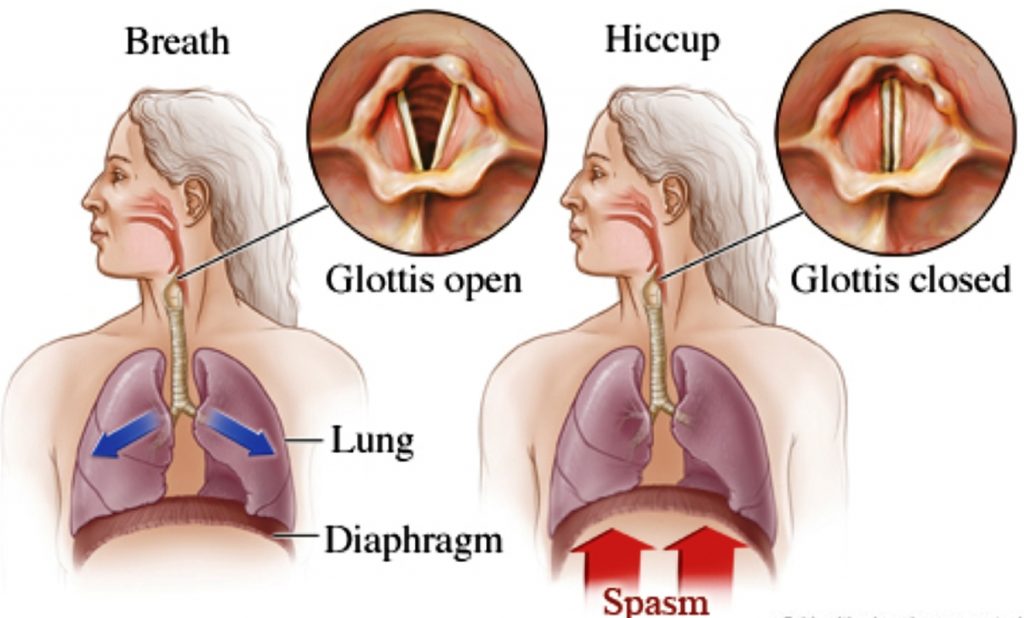
Hiccups are that strange little sounds that can escape from your mouth without any warning. And once it starts, anyone can become frustrated because of it.
Hiccups are generally repetitive and sometimes uncontrollable contractions of the diaphragm in the human body which is linked to our throat and the vocal chord.
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that is located right below the lungs and marks the boundary between our chest and the abdomen.
The diaphragm is responsible for regulating the breathing activity in humans, so, whenever an involuntary contraction is followed by a sudden closure of your vocal chord, it produces the ‘hic’ sound, which we often call it as hiccups in general terminology.
Types Of Hiccups
Generally, there are 3 categories of hiccups:
1. Short Time Hiccups (Common Hiccups)
These types of hiccups will go or stop on their own. Some home remedies can be enough for this kind but no medication or surgery is needed in this.
2. Persistent Hiccups (Continue more than 48 hours)
This type of hiccups usually needs prescribed medications. Chlorpromazine is usually the most prescribed medication.
3. Intractable Hiccups (Last longer than one month)
The phrenic nerve is a nerve that controls the diaphragm. Phenic nerve surgery is a treatment of this kind of Hiccup. This treatment rarely performed and is only for those whose hiccups don’t go away with all other treatments.
Hiccups are very common. Most of the time it starts after eating or drinking too much or too quickly. Some other causes are mentioned below.
How Hiccups Are Caused?
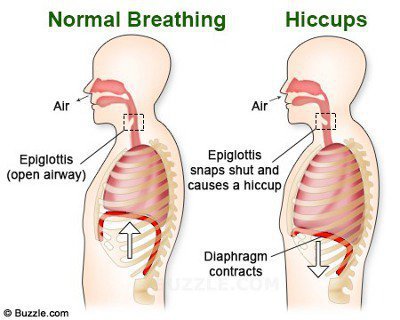
The exact cause of hiccups is still unclear but some of the possible causes include:
- Eating large meals or eating too much
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Drinking carbonated beverages
- Eating too quickly
- Swallowing air when chewing gum or sucking candy
- Smoking
- Certain medications
- Diseases that irritate the nerves that control the diaphragm
- Displaying a sudden excitement
- Displaying emotional stress
- A sudden change in temperature
- Damage to the vagus or phrenic nerve
- Problems with the liver
- Noxious fumes
- Abdominal surgery
- A brain tumor
- Strokes
- Sudden temperature changes
Hiccups that last more than a day or two may be caused by a variety of other factors than the ones mentioned above. The causes of persistent hiccups are:
1. Nerve Damage
Damage to the vagus nerves/phrenic nerves can also cause hiccups. These nerves can damage by:
- A hair or some other thing that touches your eardrum.
- A tumor or cyst in your neck.
- Gastroesophageal reflux
- A sore throat
2. Central Nervous System Disorder
A tumor/infection in your central nervous system as a result of trauma can mess your body’s normal control of the hiccup reflex. For instance:
- Encephalitis
- Meningitis
- Multiple sclerosis
- Stroke
- Traumatic brain injury
- Tumors
3. Metabolic Disorder/Drugs
Long-term hiccups may be triggered by:
- Alcoholism
- Anesthesia
- Barbiturates
- Diabetes
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Kidney disease
- Steroids
- Tranquilizers
4. Some Medication Can Also Have Hiccups As A Side Effect.
- Medication for acid reflux
- Most benzodiazepines like Diazepam, alprazolam, lorazepam
- Levodopa, nicotine, ondansetron
Risk Factors & Complications Of Hiccups
Generally, hiccups are resolved in a short time. In severe and persistent cases, when your eating and sleeping patterns are disturbed due to hiccups, weight loss is experienced along with weakness.
Rarely, complications like cardiac arrhythmias and gastroesophageal reflux (GERD and GER) have been noted in severe cases of hiccups.
The factors that may increase your risk of hiccups are :
- Mental or emotional issues – Anxiety, stress, and excitement are related to some cases of short and long-term hiccups.
- Surgery – general anesthesia or surgical procedures related to the abdominal organs can increase the chances of frequent hiccups.
Signs And Symptoms Of Hiccups
Hiccups usually occur for a short period of time. However, it may happen that at certain times, it could occur from a couple of minutes to even a couple of hours.
You must report to the doctor if your hiccups last more than 3 hours, or if they disturb your sleeping or eating habits.
Generally, the hiccup sounds that you hear due to the forceful movement of the diaphragm is the only symptom of hiccups.
When Should I Consult The Doctor?
You may face medical emergencies rarely as most of the hiccups cases are for a short time. But you need to consult the doctor if you are suffering from the following problems along with the hiccups :
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Shortness of breath
- Vomiting
- Coughing up blood
- Feeling as if your throat is going to close up.
How To Stop Hiccups In Babies?
People often take hiccups in infants more seriously and get tense. But like in adults, hiccups in infants are common and normally of no concern.
If hiccups occur while feeding, stop feeding the baby until the hiccups go away. You may try changing the position of the baby, try to get burp to your baby.
If your baby frequently hiccups while feeding then, feed your baby when he/she is already relaxed and is not overly hungry.
Diagnosis Of Hiccups
In medical terminology, the diagnosis of hiccups is based on physical evaluation. Until-unless your hiccups are a symptom of an associated medical condition, there is no need for any kind of medical test like Blood tests or X-Rays.
A doctor often carries out various examinations in order to treat hiccups in patients. Out of the various tests, a few may include cases where the patient is:
- Unable to eat properly and is losing weight
- Sleeping abnormally or is suffering from insomnia
- Having difficulty in speech
- Displaying signs and symptoms of clinical depression
- Gone through surgery in the past
Which Specialists Should You Refer To?
Carrying out these various tests can help the doctors to go for the appropriate treatment for hiccups. Specialists that are involved in treating it includes:
- Otolaryngologist (ENT specialist)
- Gastroenterologist (specialist in the digestive tract)
- Neurologist (specialist in brain and nervous system)
- Pulmonologist (lung specialist)
- A psychologist for anxiety and mental stress conditions
If your hiccups aren’t stopping from a long time like 10-12 hours then you should see your primary care provider (family practitioner).
This primary care provider can tell you which type of specialist you need according to your underlying cause. For instance, if the cause is:
- A stroke/neurological disorder, you may need a neurologist, a specialist of the nervous system, and brain.
- Acid reflux, you may need a gastroenterologist, a specialist in Digestive system disorder.
- Lung disease just like pneumonia, you may need a pulmonologist, a specialist in Respiratory tract disorders.
Procedure To Find Out The Cause
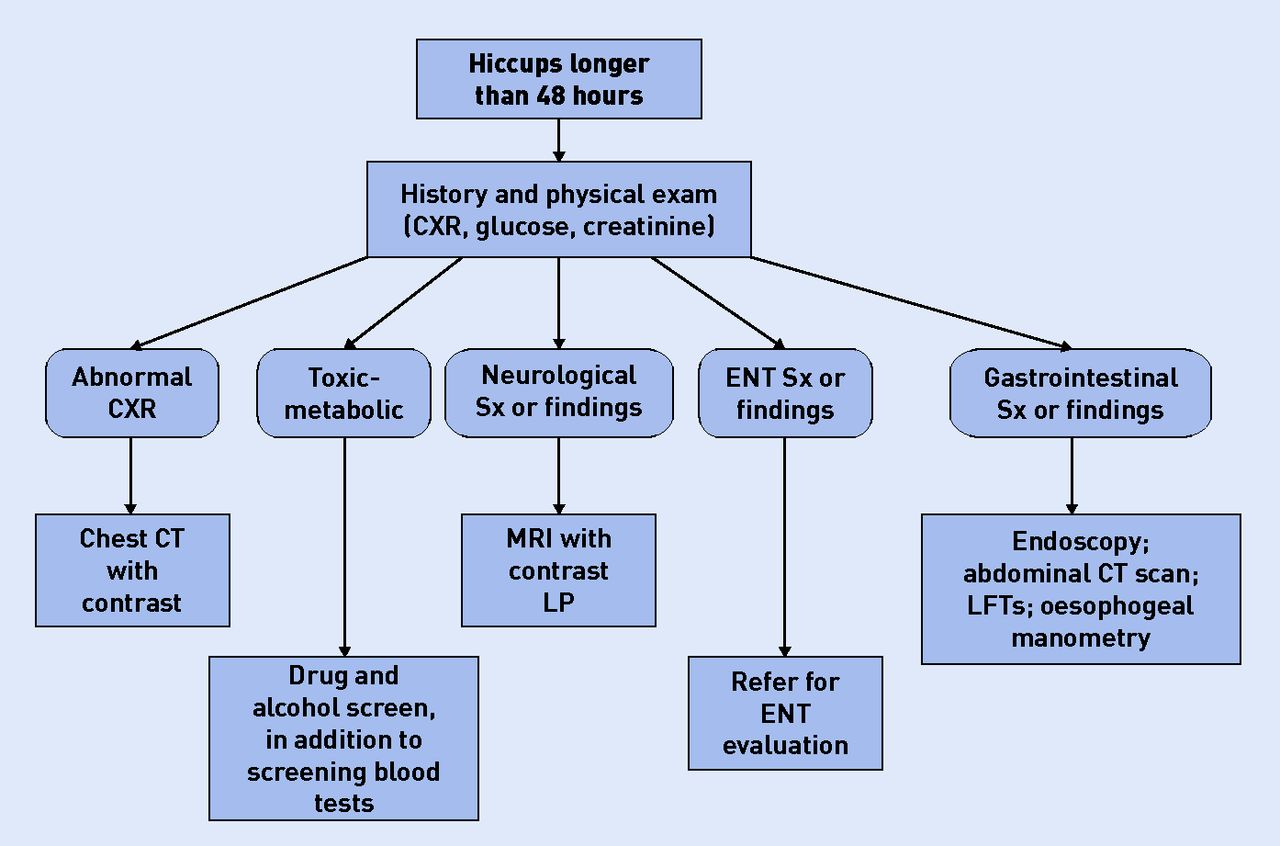
- Source: bjgp.org
If your hiccups didn’t stop for more than 48 hours than your doctor may perform a neurological exam to check your Balance and coordination, muscle strength and tone, reflexes, sight, and sense of touch.
If any underlying medical condition is suspected that is causing your hiccups than your doctor may recommend one or more of the following tests:
- A laboratory test in which a sample of your blood may be checked for signs of Diabetes, Infection, Kidney disease.
- An imaging test that may be able to detect anatomical abnormalities that affect phrenic nerve or diaphragm. Imaging test includes Chest X-Ray, Computerized tomography scan (CT Scan), Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Endoscopic tests in which a thin tube containing a tiny camera passed down your throat to check for problems in your windpipe.
Now, as you know the common causes of hiccups, let’s discuss it’s treatment as well.
How To Cure & Get Rid Of The Hiccups?
It can occur in anybody – from an infant to an older adult. If hiccups are persistent, then it is advised to seek a doctor and go for the prescribed medicine to calm it down, or totally cure it.
Generally, doctors will reserve medication as a final resort after having tried all the other options. Medications will also only be prescribed for severe and long-term hiccups.
1. Medical Treatment For Hiccups
Home remedies are enough for the general hiccups. The medical treatment is needed in the emergency like persistence hiccups (which lasts for more than 3 hours).
In this case, treatment varies and you must report to the doctor as soon as possible.
Severe and chronic hiccups may need prescribed medications. Chlorpromazine (Thorazine) is usually the first-line medication prescribed for hiccups.
Other medications used to treat hiccups include haloperidol (Haldol) and metoclopramide (Reglan) can be advised by the doctors to relieve from hiccups.
Some muscle relaxants, sedatives, analgesics, and even stimulants can also reduce hiccups symptoms.
2. Surgery For Hiccups
It may seem odd to hear that a condition like “Hiccup” might also need surgery. But it’s a very rare condition that a person having hiccups is going through a surgery to cure it.
If the medications and home remedies are unable to stop or mitigate the hiccups, then Phrenic nerve surgery (the nerve that controls the diaphragm) is the last option.
Home Remedies To Stop Hiccups
In most cases of hiccups, it will go away after a few minutes or hours without any medical treatment. There are a number of home remedies or home treatments to stop it. These are:
1. Breathing And Posture Techniques
- Practice measured breathing. Disrupt your respiratory system with measured (slow) breathing. Breath in and out both for a count of 5.
- Hold your breath. Inhale a large amount of air and hold it for 10-20 seconds and after that breathe it out slowly.
- Breath in a paper bag. Put a paper bag over your mouth and nose. now breathe slowly in and out. Puffing it on and off.
- Hug your knees. Sit down and bring your knees to your chest and hold them there for about 2 minutes.
- Compress your chest by bending forward, this puts pressure on your diaphragm.
2. Pressure Points
- Pull-on your tongue. Pulling on your tongue pushes the nerves and muscles in your throat. Take the tip of your tongue and slowly pull it forward. Repeat it twice.
- Press on your diaphragm. Apply pressure from your hands to the area just below the end of your sternum.
- Close your nose by fingers while swallowing water.
- Massage your carotid artery. The carotid artery is what when you check your pulse by touching your neck. Lie down and massage the artery of the right side of the neck in a circular motion. Do this activity for 5-10 seconds.
3. Things To Eat Or Drink
- Drink ice water. It helps in stimulating the vagus nerve when you slowly sip cold water.
- Drinking water from the opposite side of the glass. Put the glass under your chin and drink the water from the far side.
- Suck ice cube for a few minutes then swallows it once it shrinks to an adjustable size.
- Gargle ice water for about 30 seconds.
- Eat a spoonful of honey and allow it to dissolve in your mouth before swallowing.
- Take some sugar on your tongue and let it be there for 5 to 10 seconds before swallowing.
- Eat a lemon.
- Put a drop of the vinegar upon your tongue but just only one drop.
4. Other Useful Remedies
- Tap/rub the back of your neck. Rubbing the skin at the back of your neck can excite your phrenic nerve.
- Gently and slowly poke the back of your throat with a Q-tip until you a cough/gag.
- Distract yourself. Hiccups usually go away on their own when you stop focusing on them. Do some activities like calculation in mind, play video games, or fill out a crossword puzzle.
Conclusion
For many people, hiccups often stop by themselves and without having any effects. When having severe or chronic hiccups that are not cured with home remedies, in such situations, medical treatments should be taken.
It can easily be prevented by following a few simple habits:
- Avoid over-eating
- Do not eat very quickly
- Avoid drinking too much alcohol
- Avoid drinking carbonated beverages
If you need any assistance or have a question about Hiccups, you can consult our HearingSol experts with your problem, feel free to call us on +91-9327901950. We are always here to help you.

 Reviewed by Mr. Ranjeet Kumar
Sr. Audiologist, Speech Therapist & Cochlear Implant Specialist, BASLP on
Reviewed by Mr. Ranjeet Kumar
Sr. Audiologist, Speech Therapist & Cochlear Implant Specialist, BASLP on